Turkish experts formulate COVID-19 infection risk model
Scientists at Gazi University develop tool to calculate risk of infection, number of new cases
ANKARA
Researchers at Gazi University in the Turkish capital Ankara announced Wednesday that they developed a new method to estimate the risk of infection by the novel coronavirus, as well as the number of potential new cases.
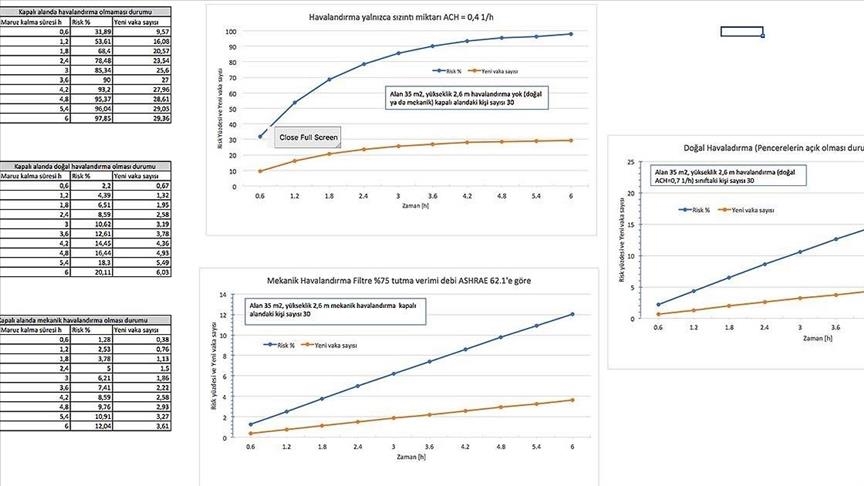
The researchers told Anadolu Agency that the new method calculates the risk of infection in indoors environments based on ventilation conditions, the number of total and infected people, and duration spent in the environment.
With this method, when 30 people, one of whom is infected, spend one hour in an indoor environment of 35 square meters (377 square feet) without ventilation, the risk of infection is 47%, and the number of new cases rises 14.
When there is natural ventilation with windows of the indoor environment open, the risk of infection drops to 30% and the new number of cases to nine. In case of mechanical ventilation under the same conditions, the risk is estimated to drop to 2% and the new cases to 0.6.
Zeki Yilmazoglu, a member of Gazi University's Faculty of Engineering, said this method could not produce precise results on infection risk, but rather provides a prediction depending on variables in the environment.
"In the calculation tool, the infection dose given to the air per hour is calculated as 48 quanta/hour in sample calculations," he said. "This value can rise to 300 quanta/hour depending on activities such as talking loudly or singing," he explained
The risk of infection is calculated for three different ventilation conditions, being no ventilation, natural ventilation and mechanical ventilation, said Yilmazoglu.
The rate of risk and number of new cases can be calculated based on these ventilation conditions and duration of exposure, he continued.
He added: "The calculations were carried out based on an adult's respiratory properties. In case of a super-spreader in the environment, the results will change depending on the dose given to the environment in a unit of time."
Yilmazoglu said the calculation tool could be deployed to gain foresight on the risk of infection and number of new cases in a given environment.
He stressed that many factors such as super-spreaders and susceptible people must be taken into consideration while carrying out the calculations.
"The study has shown one more time the importance of ventilation in indoor environments for the prevention of infection," he noted.
The calculation tool is available on the websites of Gazi University and the Turkish Plant Engineers Association.
* Writing by Dilan Pamuk in Ankara
Anadolu Agency website contains only a portion of the news stories offered to subscribers in the AA News Broadcasting System (HAS), and in summarized form. Please contact us for subscription options.

